
Astronomers observed a supermassive black hole expelling gas at nearly a third the speed of light after consuming matter too fast. This outflow could suppress star formation by heating and ejecting gas, revealing how black holes regulate galaxy evolution. The finding helps decode the feedback mechanisms of quasars and active galactic nuclei in shaping cosmic structure.
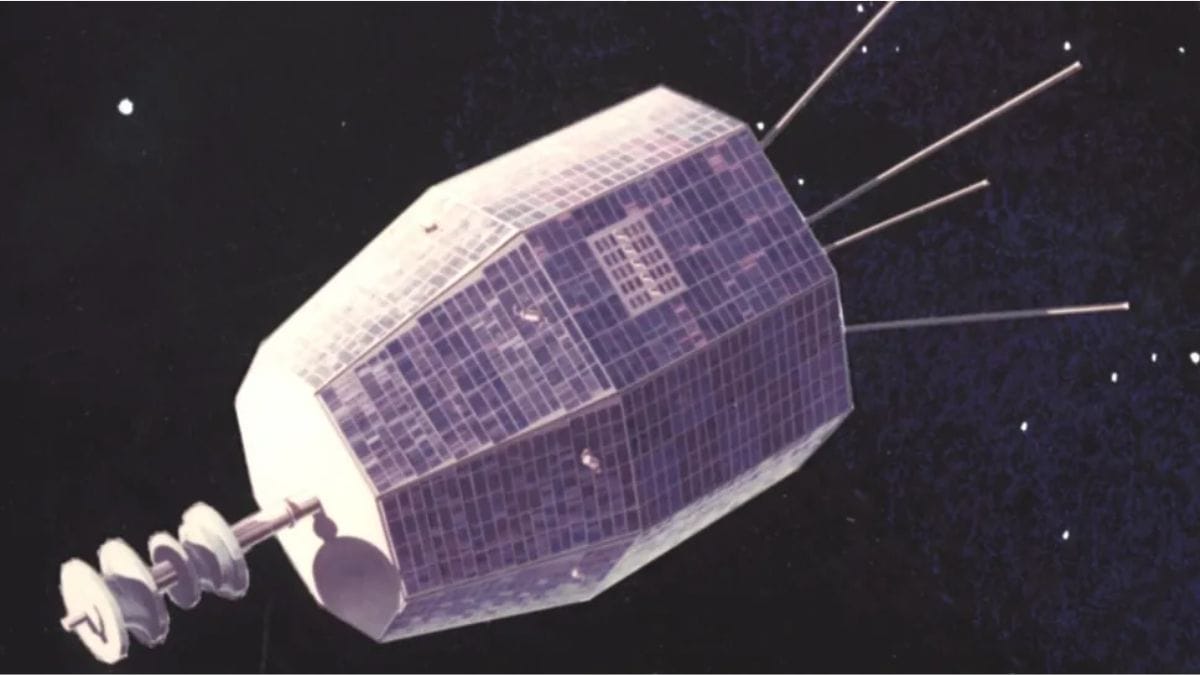
In June 2024, a mysterious 30-nanosecond radio burst baffled scientists — until they traced it back to a surprising source: Relay 2, a NASA satellite offline since 1967. Researchers believe the signal could have been triggered either by a micrometeorite impact or an electrostatic discharge. The discovery, detailed in a new preprint study, highlights how defunct satellites may still interact with space conditions. Experts say the incident could offer a new method for detecting electrostatic discharges from aging satellites and space debris in crowded orbits.

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has reached a major milestone by capturing its first direct image of TWA 7 b, a newly discovered Saturn-mass exoplanet orbiting the young star TWA 7. Using a coronagraph to block starlight, Webb identified the planet embedded in the star’s dusty ring system. TWA 7 b is the smallest exoplanet ever imaged directly. The discovery highlights Webb’s unprecedented precision and paves the way for imaging even smaller, potentially Earth-like planets with future observatories equipped with next-generation coronagraphs and infrared imaging instruments.

NASA’s James Webb Telescope has identified ethanol and methanol isotopes around protostars and HD 100453. These discoveries offer valuable clues about the cosmic origins of life, indicating that comets filled with organic molecules might have seeded early Earth.

The Rubin Observatory has unveiled its first public images, revealing vivid views of the Lagoon and Trifid Nebulae located 4,000 light-years away. These stunning images mark the beginning of a decade-long sky survey that will capture thousands of nightly exposures, explore dark matter, and transform the way scientists—and the public—observe the dynamic universe.

Twin satellites in ESA’s Proba-3 mission have successfully recreated artificial solar eclipses from space to examine the sun’s million-degree corona. The breakthrough will allow continuous observations of the sun’s outer atmosphere, offering rare insights that natural eclipses on Earth can’t provide. The mission marks a major step in solar science and is expected to capture over 1,000 eclipse hours.

Researchers from NTNU and EPFL have developed a compact, low-cost laser on a photonic chip using thin-film lithium niobate. This new laser enables ultrafast, mode-hop-free tuning and delivers stable performance with a single control knob. Demonstrated in LiDAR systems, it achieved 4 cm range precision for self-driving cars and also detected trace hydrogen cyanide for environmental monitoring. The breakthrough could transform precision applications like gas sensing and autonomous navigation, making advanced systems more affordable and accessible. The laser’s scalable chip-based design supports mass production using existing fabrication methods.

Axiom Mission 4 has now reached the International Space Station on June 26, 2025. Launched from Kennedy Space Centre, the mission features a diverse international crew aboard SpaceX's Dragon spacecraft.

NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter and India’s Chandrayaan-2 have captured images confirming the crash of Japan’s Resilience lander on the Moon’s Mare Frigoris. Contact with the lander was lost 100 seconds before its June 5 touchdown. New photos reveal a dark impact mark and scattered debris.

Amazon’s Project Kuiper is intensifying efforts to compete in the low Earth orbit (LEO) broadband race. With 27 satellites launched in April 2025 and plans for a 3,200-satellite constellation, Amazon has locked in dozens of launches across ULA, Blue Origin, Arianespace, and SpaceX. This move follows its successful 2023 prototypes and aligns with a global push for satellite internet dominance. As Starlink maintains the lead and China expands its constellations, Kuiper aims to begin services by late 2025, signaling a pivotal moment in the future of global internet connectivity.

A failed Soviet Venus probe from 1972 re-entered Earth’s atmosphere in May, yet tracking its final descent baffled experts. Despite decades of observation, differing models and unpredictable atmospheric conditions prevented precise predictions. Scientists now see Kosmos-482 as a case study in the enduring challenges of satellite reentry and the need for better space debris tracking.

The Rubin Observatory’s first image captures 10 million galaxies, marking the start of a decade-long sky survey. With its powerful telescope and LSST camera, it will scan the southern sky every three nights, unveiling hidden galaxies, stellar nurseries, and transient cosmic events. Scientists anticipate transformative discoveries about dark matter, dark energy, and the evolving universe.

Axiom-4 mission (also known as Ax-4), which is carrying four astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS), is finally taking off today (Wednesday). The mission was originally scheduled to take off on June 10, but it was delayed several times due to technical issues. The mission also marks an important moment for India as the Indian Space Research Organisation’s (ISRO) Shubhanshu Shukla will become the first Indian to take a spaceflight in the last 40 years.

NASA has officially postponed the launch of Axiom Mission 4 due to operational concerns. Now set for June 25, 2025, the mission is historic for India, Poland, and Hungary. It will send astronauts, including India's Shubhanshu Shukla, to the ISS for a 14-day scientific expedition.

A buried magma plume beneath Oman’s Salma Plateau may have nudged India’s tectonic path during its collision with Eurasia, scientists report. Named “Dani,” the amagmatic plume caused no eruptions but likely altered continental motion 40 million years ago. This discovery redefines how silent, deep mantle forces can reshape continents without leaving volcanic signatures on the surface.

Blue Origin’s NS-33 launch has been postponed again due to high winds in Texas. The suborbital mission, which will carry six passengers aboard New Shepard, marks the company’s 13th crewed flight. A new launch date has not yet been confirmed, as teams continue to monitor weather conditions at the West Texas site.

A Tongji University study shows green roofs can trap most rainborne microplastics, with soil capturing the majority. If all Shanghai rooftops went green, they could remove 56.2 metric tons of microplastics each year, highlighting a promising method for tackling urban pollution.

SpaceX’s Transporter-14 mission on June 23 will carry over 150 capsules of DNA and cremated remains into orbit for Celestis. The flight, in partnership with The Exploration Company, will briefly orbit Earth before reentry. It marks Celestis’ 25th space memorial mission and offers a symbolic journey for participants, including the youngest European to send DNA to space.

The Vera C. Rubin Observatory will unveil its first images on June 23 via a global livestream. Captured using a groundbreaking 3,200-megapixel camera, the images mark a major milestone in the observatory’s mission to explore dark matter and dynamic cosmic phenomena. The LSST survey will scan the southern sky for a decade, transforming our view of the universe.

Gas workers in Peru discovered a 1,000-year-old mummy during pipeline work in Lima. The boy’s remains, found in a seated burial position with ceremonial items, belong to the Pre-Inca Chancay culture. The site is one of over 2,200 archaeological finds made by Calidda since 2004.

A newly modelled 21-centimetre radio signal from hydrogen atoms just 100 million years after the Big Bang may reveal the mass of the universe’s first stars. Using REACH and the upcoming SKA telescopes, researchers aim to uncover how early starlight shaped cosmic evolution during the Cosmic Dawn, when the universe transitioned from darkness to light.

Excavations at Israel’s Tel Dan sanctuary have revealed that Phoenicians practised ritual cleansing for centuries. A bathing unit linked to priestly rites and later pilgrim use offers insight into evolving spiritual customs. New research expands our understanding of sacred traditions in the Near East, including the use of water in local religious ceremonies.

The James Webb Space Telescope has revealed that planets can form in extreme radiation zones. A protoplanetary disk called XUE 1, exposed to intense ultraviolet light, still shows signs of water and potential for rocky planet formation. The findings challenge old assumptions and broaden the possible regions where Earth-like planets may emerge.

A powerful X1.9-class solar flare from sunspot 4114 erupted on June 19, disrupting shortwave radio signals across the Pacific, including Hawaii. While it caused significant atmospheric ionisation, no coronal mass ejection (CME) followed. The event highlights rising solar activity and hints at more eruptions ahead, potentially impacting communications and space weather conditions.

A 146,000-year-old skull discovered in Harbin, China, has been confirmed as Denisovan using ancient DNA and protein analysis. Named “Dragon Man,” the fossil is the most complete Denisovan specimen to date, offering a new understanding of human evolution and Denisovan presence across Ice Age Asia.

A physicist explains the science behind Mars’s red appearance, linking its hue to iron oxide or rust. While known as the Red Planet, rover images and telescope data show varied colors, from tan to white ice caps. Observations in ultraviolet and infrared light reveal deeper insights into Mars’s atmosphere, surface, and seasonal changes, enriching planetary science.

NASA confirms comet C/2014 UN271, the largest known from the Oort Cloud, is chemically active. Detected by ALMA from far beyond Neptune, the comet’s carbon monoxide jets offer rare insights into icy body chemistry and early solar system conditions.

A SpaceX Starship rocket exploded during a static fire test at the Starbase facility in Texas, causing significant damage but no injuries. Preliminary findings suggest a pressurised tank failure in the rocket’s nosecone. Despite recent setbacks, SpaceX remains committed to its Mars mission, backed by NASA and a newly approved expansion in Starship launch frequency

NASA has delayed the Axiom Mission 4 launch, citing the need for more time to evaluate the ISS after recent repairs to its Zvezda module. The agency and its partners are reviewing upcoming launch windows while ensuring the space station is fully prepared to receive the international crew led by Peggy Whitson.

Astronomers have uncovered the universe’s missing baryonic matter using rapid radio bursts. The study, published in Nature Astronomy, shows that most ordinary matter lies between galaxies, hidden in faint intergalactic clouds. This breakthrough highlights FRBs as powerful tools to probe cosmic structures, paving the way for discoveries in large-scale universe mapping and evolution.

Scientists have uncovered the volcanic origin of tiny orange glass beads collected during the Apollo missions. Preserved for over 3.5 billion years, these lava droplets offer crucial insights into the Moon’s fiery past and evolving geology. Advanced analysis now reveals changing volcanic activity and deep interior conditions from the Moon’s formative era.

Carbon-dated to 3482–3102 B.C., the Tarkhan Dress is the world’s oldest known tailored garment. Discovered in an Egyptian tomb near Cairo, it offers insights into early textile artistry and everyday life during Egypt’s First Dynasty. Experts believe the linen dress was worn in life before being used in burial, revealing a rare glimpse of ancient fashion.

Ancient footprints discovered in White Sands, New Mexico, have been confirmed to be over 23,000 years old, pushing back the timeline of human presence in the Americas by nearly 10,000 years. Radiocarbon dating of mud samples across three labs supports their authenticity, challenging long-held beliefs about the Clovis culture and reshaping early migration theories.

The iRonCub3 humanoid robot, developed by Italy’s IIT, has completed its first controlled flight using jet propulsion and AI-powered systems. The 70 kg robot uses neural networks for real-time aerodynamic stability, marking a breakthrough in aerial robotics. Its design enables future use in disaster response, exploration, and hazardous environments where traditional machines cannot operate.

NASA’s Curiosity rover has entered the Uyuni quad on Mars, beginning a new leg of its mission. The rover completed a 48-metre drive and is now collecting fresh data on sedimentary textures and surface chemistry. With a focus on remote sensing and contact science, the team hopes to uncover clues about past Martian environments.

NASA’s SCIFLI team will track the reentry of a European test capsule named Mission Possible using a spectrometer and high-definition telescope from a Gulfstream III aircraft. The mission aims to gather thermal and parachute deployment data, aiding spacecraft design. Backed by a Space Act Agreement, it highlights international collaboration and enhances safety for future atmospheric entries.

ESA’s Proba-3 mission has captured the first artificial solar eclipse from space using two satellites flying in precise formation. This breakthrough allows frequent, high-resolution imaging of the sun’s corona, bypassing the rarity of natural eclipses. The mission opens new frontiers in solar physics and space weather research with open access to around 1,000 hours of data.

According to NASA, changes in Earth’s magnetic field 540 million years ago corresponded with atmospheric oxygen shifts. This finding suggests that Earth’s deep interior may impact surface habitability. Scientists plan further research to trace these connections and their role in life’s origin.

SpaceX launched 26 Starlink satellites from California on June 16, advancing its global broadband expansion. The Falcon 9 rocket successfully delivered the payload to low Earth orbit, and its booster completed a third landing on a Pacific droneship. The mission supports Starlink’s growing constellation, which now includes over 7,760 active satellites worldwide.

NASA and the U.S. Department of Defence carried out joint emergency rescue simulations for Artemis II, rehearsing astronaut recovery during launch abort scenarios. Conducted off Florida’s coast, the drills involved the Orion test capsule, mannequins, and military rescue teams. These exercises enhance preparedness to safely return crew members during any launch failure on NASA’s first crewed Moon mission in decades.

A new study reveals that the brain relies on signal strength in the fusiform gyrus to decide whether visuals are real or imagined. This “reality threshold” may help explain how imagination can influence perception and sheds light on disorders like schizophrenia. Researchers believe this mechanism could be central to understanding hallucinations and cognitive disruptions in visual processing.

A recent study reveals the feather-legged lace weaver spider doesn’t inject venom but instead kills by coating its prey with regurgitated toxins on silk. Despite lacking venom glands and ducts, this unique method proves equally lethal and may redefine how scientists understand spider evolution and prey capture strategies, according to findings published in BMC Biology.

A NASA-developed model now enables scientists to estimate the likelihood of life on distant planets or moons using limited and uncertain remote-sensing data. By comparing habitat conditions with known lifeforms or hypothetical organisms, the framework offers a probabilistic tool to assess alien environments and improve telescope targeting in the ongoing search for extraterrestrial life.

India’s Shubhanshu Shukla is set to launch aboard the Axiom-4 mission on June 22 after a series of delays prompted by technical issues and safety reviews. The SpaceX-led mission will send astronauts from India, Hungary, and Poland to the International Space Station, where they will carry out over 60 experiments spanning biology, Earth science, and human research.

Discovered near the Dead Sea, the Qumran scrolls contain ancient biblical texts and writings from a Jewish sect, likely the Essenes. Archaeological and AI research shows the scrolls' origins stretch back over 2,000 years, offering rare insight into Second Temple Judaism. Their preservation in the caves continues to fuel historical and religious scholarship.

Buried in China’s Tarim Basin desert, the Bronze Age Xiaohe culture left behind boat-shaped coffins, cattle artefacts, and mysterious upright poles. Archaeologist Dr. Gino Caspari’s new analysis suggests these symbols represent a mirrored afterlife and a water-centric worldview.

New research links nearby supernovas to drastic shifts in Earth’s ancient climate. These cosmic explosions may have eroded the ozone layer, triggered global cooling, and even caused mass extinctions. Tree ring data supports the theory, raising concerns that future stellar events, like the expected Betelgeuse explosion, could again pose serious atmospheric threats to our planet.

Astrophotographer Greg Meyer captured a vivid 34-hour exposure of the Lagoon and Trifid nebulas glowing in the constellation Sagittarius. Framed beneath a dense starfield, the image reveals young stars sculpting gas and dust across 4,000 light-years. Taken from Arizona’s dark skies, the portrait offers a dazzling glimpse into stellar birth regions within our Milky Way galaxy.

Using the NSF’s Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope, scientists have captured the most detailed views of the Sun’s surface ever recorded. The new observations reveal ultra-narrow magnetic striations only 20 kilometers wide, etched into solar granules. These light and dark bands reflect subtle variations in magnetic field strength. Researchers say the patterns serve as "fingerprints" of fine-scale magnetism, vital for understanding solar eruptions and forecasting space weather. With its 4-meter aperture, DKIST is the world's most powerful solar telescope, unlocking new layers of the Sun’s magnetic complexity.

NASA, Axiom Space, and SpaceX have rescheduled Axiom Mission 4 to June 19, 2025, following promising leak repairs on the ISS and SpaceX’s successful resolution of a rocket fuel leak. The four-member crew includes astronauts from the U.S., India, Poland, and Hungary. Final confirmation is pending additional evaluations aboard the space station.