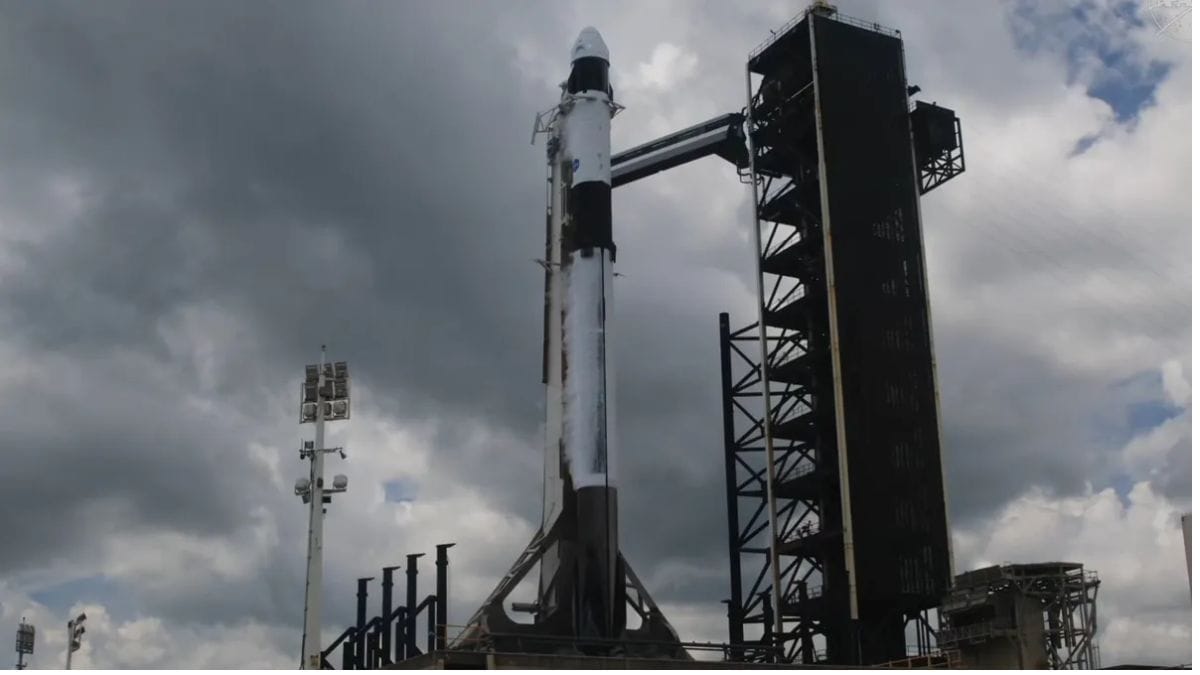

SpaceX and NASA scrubbed the Crew-11 astronaut launch on July 31 due to unsafe cumulus clouds. The next launch attempt is now set for August 1. The mission will send four astronauts to the ISS aboard the reused Crew Dragon Endeavour spacecraft.
A solar sail spacecraft could extend space weather warnings from 40 to 60 minutes, offering vital lead time before solar storms strike. Part of the SWIFT mission, this satellite will orbit farther than any current monitor, using sunlight for propulsion. The system aims to better protect satellites, astronauts, and power grids from geomagnetic disruptions caused by solar eruptions.
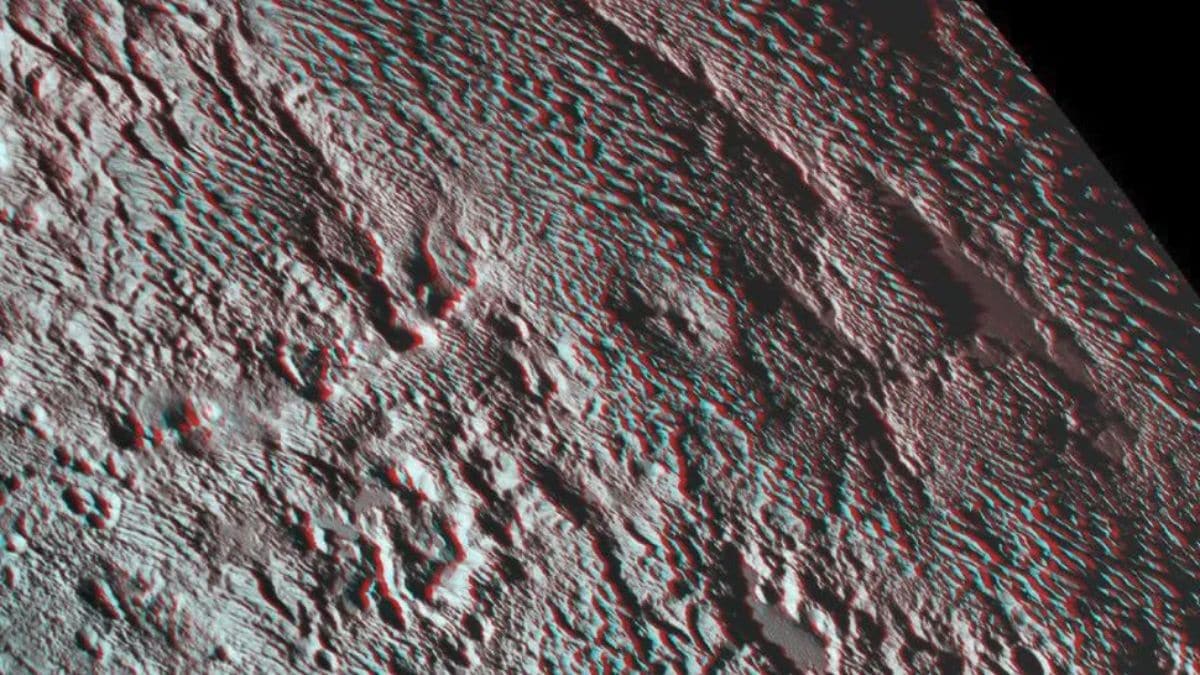
New research based on New Horizons’ decade-old data has uncovered extensive bladed terrain made of methane ice on Pluto. These towering spires, arranged in spaced-out, parallel rows, are likely shaped by seasonal condensation and sublimation cycles. While the terrain spans over half the planet’s midsection, five times the width of continental USA, scientists remain unsure of its uniformity.

Blue Origin’s 14th crewed spaceflight, NS-34, lifted off from West Texas on August 3, 2025. This symbolic flight marked the long-postponed space journey of Justin Sun, crypto billionaire and founder of Tron. Joined by adventurers and professionals from different corners of the world, including India and Puerto Rico, the mission highlighted global participation in private space travel.

China successfully launched Pakistan’s first dedicated remote sensing satellite, PRSS-01, aboard a Kuaizhou-1A rocket from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center in Sichuan. The satellite entered its planned orbit and will provide high-resolution imaging for civilian and governmental uses, including urban planning, land surveys, environmental monitoring, and rapid disaster response. Engineers from both countries collaborated closely on the mission, reflecting deepening China-Pakistan technological ties. The launch highlights Pakistan’s growing ambitions in space and the importance of satellite-based data in modern infrastructure and emergency planning. It also strengthens China’s position as a global provider of commercial launch services and supports its broader Belt and Road Initiative by fostering regional cooperation in advanced space technologies.

Astronomers have long speculated about a hidden planet—Planet Nine—lurking beyond Neptune. First proposed in 2016, the theory explains the strange orbits of distant Kuiper Belt objects through the gravitational pull of a massive, unseen world. Caltech researchers remain confident, while others suggest alternatives like debris rings or even a black hole. Recent discoveries such as 2023 KQ14 deepen the mystery. Despite limited data, the search continues with advanced telescopes, pushing the boundaries of our knowledge of the solar system’s remote edges.

Gold has amazed scientists by remaining solid under extreme temperatures—14 times its standard melting point—due to superheating. The study highlights how conventional physics may not fully explain ultra-fast reactions. These groundbreaking results, published in collaboration with international labs, have far-reaching implications for high-energy environments like asteroid impacts and nuclear systems.

A new study from Brazil proposes an inelastic dark matter model using a massive vector mediator, potentially explaining the correct abundance of dark matter while evading existing detection limits. This fresh approach could revive interest in previously ruled-out models and offers experimental pathways to test these elusive particles through the intensity frontier in future particle physics experiments.

Astronomers have discovered a massive, 200-light-year-wide cloud of gas and dust—dubbed the Midpoint cloud—hidden in the Milky Way. This giant molecular cloud appears to channel dense material into the galaxy’s core, possibly fueling star formation. The discovery offers rare insights into how matter flows from the galaxy’s disk to its turbulent center, shaping stellar evolution.

The supergiant star called Wd1-9 has been recently investigated in detail. This detailed, in-depth research was done using NASA’s Chandra X-Ray Observatory. The new findings suggest that it is a part of the binary system.

Eris, Australia’s first orbital rocket, has failed at its launch. The Gilmour Space is the company that crafted this rocket. The possible reason behind the failure is suspected to be a technical failure.

The Weather satellite has recently detected the record-breaking megaflash that appeared in the year 2017 and has surpassed the record of the 477-mile lightning bolt, which occurred in 2020. The new world record holder for the lightning bolt stretched 515 miles long, measuring Texas to Missouri.

Astronomers discovered a rogue planet hidden in Hubble’s archival data using gravitational microlensing based on Einstein’s theory. The event, OGLE-2023-BLG-0524, lasted just eight hours and lacked signs of a host star, suggesting the planet might be truly free-floating.

On October 9, 2022, astronomers detected GRB 221009A, the most powerful gamma-ray burst ever recorded, earning the nickname “BOAT” (Brightest Of All Time). This rare, once-in-10,000-year event came from a galaxy 2 billion light-years away and temporarily blinded gamma-ray detectors. It revealed new insights into stellar death, as the associated supernova (SN 2022xiw) was initially hidden by the burst’s brilliance. Using Fermi and the James Webb Space Telescope, scientists detected unique signals like electron-positron annihilation but no heavy elements, challenging assumptions about how such elements are created in stellar explosions and refining GRB and black hole models.

Elon Musk's brain implant company Neuralink said on Thursday it will launch a clinical study in Great Britain to test how its chips can enable patients with severe paralysis to control digital and physical tools with their thoughts.

MIT scientists have conducted the most precise version of the double-slit quantum experiment using ultracold atoms. The findings support Bohr’s Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics and challenge Einstein’s belief in deterministic realism. The experiment offers robust evidence for quantum indeterminacy and reinforces Bell’s theorem, marking a critical step in our understanding of reality at the quantum level.

PSR J0922+0638, an ultradense neutron star, shows puzzling rotational glitches every 550 days. Using 22 years of radio data, scientists detected both abrupt and slow changes in its spin. These may be linked to magnetic field cycles or superfluid dynamics deep inside the star. However, the exact cause remains a mystery, demanding continued long-term study.

Astronomers have raised concerns over Starlink’s unintended radio emissions interfering with space observation. A Curtin University study found emissions from SpaceX satellites impacting up to 30% of astronomical data. Experts urge updated regulations to protect radio astronomy, as current rules overlook these non-deliberate signals from satellite constellations like Starlink's.

ISRO successfully launched NISAR with NASA aboard GSLV-F16. The satellite will track Earth’s changes, aid disaster prediction, and support agriculture.

SpaceX successfully launched 28 Starlink V2 Mini satellites into low Earth orbit on July 30, 2025, from Cape Canaveral. The Starlink 10-29 mission lifted off at 11:37 p.m. EDT aboard a Falcon 9 rocket, marking the 96th launch of the year for SpaceX. After payload separation, the rocket’s first stage, booster B1069, landed flawlessly on the droneship “Just Read the Instructions” — its 26th mission, a testament to the company’s reusability strategy.

The Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum has reopened five state-of-the-art galleries, blending historic aviation milestones with futuristic space technology. Highlights include SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket parts, a 3D-printed Mars habitat, and the revived “Friendship 7” capsule. Part of a $900 million overhaul, the exhibits mark a bold step toward the museum’s 50th anniversary in 2026.

In a rare celestial event, NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) captured two eclipses on July 25, 2025. First, at 2:45 UTC, the Moon passed between SDO and the Sun, covering about 62% of the solar disk. Just hours later, around 6:30 UTC, Earth itself blocked the Sun entirely from SDO’s perspective. These dual eclipses occurred during SDO’s eclipse season and were observed in remarkable ultraviolet detail. The Moon’s silhouette appeared sharp, while Earth’s edge looked diffused due to atmospheric scattering. Since 2010, SDO has been a critical tool in observing solar phenomena and helping forecast space weather events.

NASA and ISRO’s NISAR satellite is set to launch on July 30 from India’s Satish Dhawan Space Centre. The mission will use dual-frequency radar (L-band and S-band) to scan nearly all of Earth’s land and ice surfaces every 12 days. Developed by NASA’s JPL and ISRO’s Space Applications Centre, NISAR is the first satellite to carry both radar types, enabling precise tracking of soil moisture, vegetation, and ground motion.

The gas giant TOI-2109b, over five times Jupiter’s mass, is spiraling closer to its star in a rare planetary death spiral. With a 16-hour orbit and blistering heat, the exoplanet could either plunge into its host star, be torn apart by tidal forces, or evolve into a rocky super-Earth through photoevaporation. NASA’s TESS and ESA’s Cheops data confirm its orbit is decaying by 10 seconds every 3 years. TOI-2109b’s extreme case offers astronomers a powerful chance to study how gas giants die—or transform—revealing secrets of planetary evolution across the galaxy.

Hubble has captured images of comet 3I/ATLAS, an ancient interstellar object likely 7 billion years old. As only the third known visitor from beyond the solar system, it offers rare insights into distant planetary systems. With its water ice and D-type asteroid-like dust, 3I/ATLAS is now under global scientific scrutiny before it vanishes back into deep space.

UBTECH’s Walker S2 is a humanoid robot that can replace its own battery, reducing human intervention. Ideal for automation in industries and customer service, this 2025 innovation sets a new benchmark in robotics with its smart energy management and autonomous charging capabilities.

NASA and Lockheed Martin’s X-59 experimental aircraft, engineered for quiet supersonic travel, is undergoing taxi tests at the U.S. Air Force’s Plant 42. Unique features include its AR-enabled camera vision system and a boom-reducing shape. The X-59 continues NASA’s legacy at Plant 42, home to iconic aerospace programs like the F-22 and Space Shuttle assembly.

The presence of unusual plasma waves at Jupiter’s North Pole, detected by NASA’s Juno Spacecraft, has been explained by a group of scientists from the University of Minnesota. The team was led by Rober Lysak, wherein findings have resulted in the identification of the new types of plasma waves.

On July 25, 2025, Russia launched two Ionosfera-M satellites and Iran’s Nahid-2 communication satellite aboard a Soyuz-2.1b rocket from Vostochny. The new Ionosfera-M probes expand Russia’s space weather tracking constellation, while Nahid-2 reflects Iran’s space ambitions. The joint launch highlights deepening space collaboration between Moscow and Tehran amid global tensions and sanctions.

NASA’s JunoCam, once believed nearly lost to Jupiter’s intense radiation, has made a stunning comeback thanks to a bold experiment. Engineers used a process called annealing—heating the camera from afar—to reverse internal damage and restore image clarity. Just in time for a close flyby of the volcanic moon Io, the camera delivered detailed images of lava flows and sulfuric peaks. The breakthrough technique is now being applied to other instruments on Juno and could shape future spacecraft built for radiation-heavy environments around Earth and beyond.

A growing number of rocket launches may be compromising the ozone layer's recovery, according to new scientific studies. Chlorine and soot from rockets, along with pollutants released during satellite re-entry, could have long-term environmental impacts. The space industry is urged to act now—through regulation, innovation, and cleaner fuels—to protect one of Earth's vital protective layers.

The revelation that Mars once had Earth-like rainfall reshapes our understanding of planetary evolution. The insights support the theory that early Mars was far more hospitable than previously believed, possibly housing primitive life forms. The findings could guide future missions like NASA’s Perseverance in locating signs of fossilised organisms.

SpaceX launched two mPOWER internet satellites into medium Earth orbit and landed its Falcon 9 booster on a ship in the Atlantic, marking its 89th Falcon mission of the year. The satellites will expand SES’s global network as the company moves closer to completing its 13-satellite constellation for advanced internet coverage worldwide.

Astronomers have finally spotted Betelgeuse’s hidden companion star, ending a 1,000-year mystery about its six-year dimming cycle. Using Gemini North’s advanced imaging, researchers captured the first image of the elusive companion orbiting deep within Betelgeuse’s atmosphere. The discovery solves a stellar puzzle and offers new insight into red supergiant systems.

NASA's latest launch from Vandenberg Space Force Base saw the TRACERS mission successfully lift off, one day after a delay due to FAA airspace restrictions. The mission promises valuable insights into solar wind interactions and space weather impacts.

SpaceX halted its Falcon 9 launch just 11 seconds before liftoff on July 21, delaying the deployment of two SES O3b mPOWER satellites. The mission, intended to expand SES’s broadband network in medium-Earth orbit, was rescheduled for July 22. SpaceX confirmed the rocket and payload remain in good condition, though the cause of the abort remains undisclosed

On Tuesday, July 22, 2025, Earth will complete its rotation 1.34 milliseconds faster than the usual 24 hours, scientists say. That will make it the second-shortest day ever recorded, just behind July 10, 2025. The trend of shorter days has accelerated since 2020, attributed to factors like the Moon’s position, mass shifts from melting ice, and atmospheric changes.

Scientists have successfully grown algae in bioplastic chambers under Mars-like conditions, marking a step toward sustainable habitats for astronauts. The chambers, made from polylactic acid, supported photosynthesis and stabilized liquid water. This breakthrough suggests self-replicating biomaterials could reduce Earth-based resupply, advancing long-term space colonization and offering new paths for sustainable technologies on Earth.

NASA is developing scalable, modular satellite platforms to reduce cost and accelerate science missions. The Athena EPIC spacecraft, built from eight “Satlet” modules, shares control systems among instruments, simplifying integration. Slated to launch in 2025 on a SpaceX rideshare, Athena aims to cut costs from billions to millions per mission. Other NASA programs like PTD and CLICK show similar promise using CubeSat-based designs. These small satellites allow for faster development, lower risk, and greater scientific return—especially for climate and weather observations. NASA says these systems represent a “less traditional, more efficient path to launch” for the next generation of sensors.

NASA’s TRACERS satellites will fly in tandem through Earth’s polar cusps to study magnetic storms and solar wind effects. The mission aims to improve predictions of space weather events that threaten satellites, power grids, and astronauts, offering new insight into magnetic reconnection and helping protect vital systems from the hazards of intense solar activity.

LHCb at CERN reports first CP violation in baryons—a 2.45% decay asymmetry—offering new clues to matter–antimatter imbalance. This result, statistically significant at 5.2σ, confirms fundamental physics theories while opening fresh avenues for exploring the matter–antimatter imbalance that shaped our Universe.

NASA/ESA’s Hubble Space Telescope has released a stunning new image of Abell 209, a massive galaxy cluster 2.8 billion light-years away in Cetus. The golden cluster houses over 100 galaxies, but beneath them lies an invisible web of hot gas and dark matter. Using gravitational lensing, Hubble reveals curved arcs of light from background galaxies, helping astronomers map unseen mass. The image—taken with Hubble’s ACS and WFC3 cameras—blends optical and infrared views, offering sharp cosmic detail. The findings aid our understanding of dark matter, dark energy, and how the universe evolves under their influence.

For the first time, scientists have detected lithium in Mercury’s exosphere using magnetic wave signatures found in MESSENGER spacecraft data. The findings link lithium’s release to meteoroid impacts that vaporise planetary material, offering fresh insight into volatile element delivery. This breakthrough reshapes our understanding of Mercury’s surface chemistry and thin atmospheric dynamics across airless planetary bodies

A team of Indian astronomers has successfully explained the rare aurora seen over Ladakh, caused by intense solar activity and CME collisions. The event, captured in May 2024, was traced using global data and advanced solar models, offering new insights into space weather forecasting and solar storm impacts on Earth.

A high-resolution climate model reveals that a 1°C global temperature rise could drive Arctic warming up to 5°C and intensify rainfall extremes in regions like the Himalayas and Andes. The simulation offers vital regional insights for climate adaptation, disaster risk management, and infrastructure planning in vulnerable zones, including small islands and mountain communities.

A stunning new image from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope reveals that ancient star cluster NGC 1786—located 160,000 light-years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud—hosts stars of varying ages. Once believed to contain a single generation of stars, NGC 1786 now appears to preserve a more complex stellar history. This multi-age discovery suggests that early galaxies may have formed stars in stages, not all at once. By comparing it to Milky Way clusters, astronomers hope to retrace how both galaxies evolved. The findings provide fresh insight into how galaxies like ours grew through gradual star formation and mergers.

Brookhaven’s sPHENIX detector at RHIC has released its first results from gold-ion collisions, confirming accurate detection of particle counts and energy levels. These measurements validate the detector’s performance and lay the groundwork for exploring quark–gluon plasma (QGP)—a primordial state of matter from the early universe. With baseline data established, sPHENIX will now track high-energy jets to investigate how quarks and gluons behave in the QGP. The upcoming 2025 run will exploit the detector’s full capabilities, offering key insights that complement high-energy studies at CERN’s LHC.

NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory has captured a rare glimpse of TOI 1227 b, a young, Jupiter-sized exoplanet losing its atmosphere under intense stellar radiation. Just 8 million years old, the planet is shrinking rapidly as X-rays strip away its mass. Scientists warn it may become a barren rocky core in about a billion years.

A meteorite strike in northern Arizona may have triggered a massive Grand Canyon landslide 56,000 years ago. Researchers found ancient driftwood and lake sediments indicating a paleolake formed after the Colorado River was dammed. The study suggests seismic waves from the Meteor Crater impact caused the landslide. Findings were published in the journal Geology.

Gemini North has imaged 3I/ATLAS, the third interstellar object to enter our solar system. Larger than its predecessors and possibly older than our solar system, the comet will pass closest to the Sun on Oct. 30 before returning to deep space. Scientists worldwide are racing to gather data during its brief visit.