
The Moon's surface undergoes extreme temperature shifts, ranging from over 100°C in daylight to minus 100°C in darkness. These fluctuations are due to the lack of atmosphere, which causes rapid temperature changes. The Moon's regolith, poor at conducting heat, leads to insulation at deeper levels. Shaded areas, particularly in lunar pits, maintain more stable temperatures, potentially crucial for future habitation. The poles, especially near the south, experience permanent shadows, making them ideal for ice trapping and human exploration

NASA’s ESCAPADE mission will send two identical orbiters to Mars to study how solar wind and space weather strip away the planet’s atmosphere. Launching in 2025 and arriving in 2027, the twin spacecraft will measure solar wind conditions and Mars’s atmospheric response simultaneously, helping scientists understand how the Red Planet lost its thick atmosphere and how solar storms continue to shape its environment today.
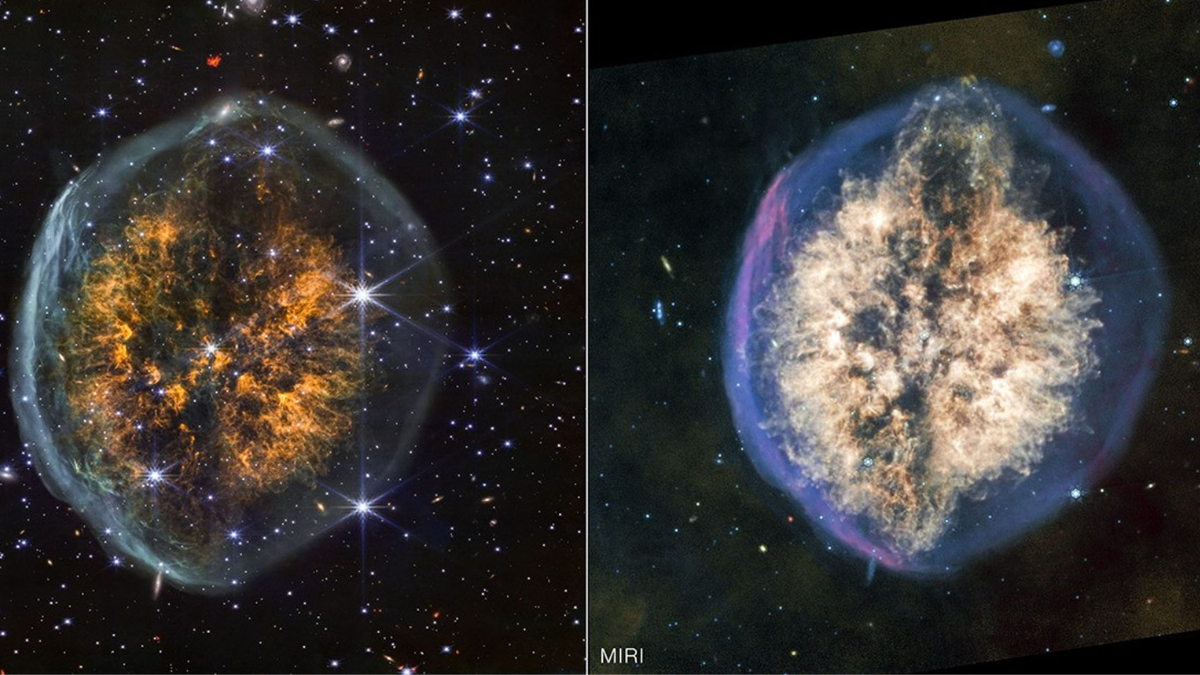
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured remarkably detailed infrared images of PMR 1, known as the “Exposed Cranium,” a planetary nebula roughly 5,000 light-years away in the constellation Vela. The observations reveal a glowing inner “brain” region surrounded by a hydrogen gas shell, divided by a dark lane of ejected material, providing fresh insight into the brief, dramatic final phase of a dying star’s evolution.

The James Webb Space Telescope has produced the first 3D map of Uranus’s upper atmosphere, tracking temperatures and ion densities up to 5,000 kilometers above its clouds. The observations reveal bright auroras shaped by the planet’s tilted magnetic field and confirm that Uranus is still slowly cooling over long timescales.

NASA astronomers using the Chandra X-ray Observatory have discovered a vast, million-degree gas bubble surrounding HD 61005, a 100-million-year-old Sun-like star about 120 light-years away. Its stellar wind is far stronger than today’s solar wind, forming a 200 astronomical unit-wide astrosphere that offers rare insight into how the young Sun once shaped the early solar system.

NASA has rolled back the Artemis II SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft after engineers detected a helium flow issue in the upper stage during fueling tests. The problem affects fuel tank pressurization and engine performance, delaying the planned March launch as teams inspect and repair the rocket.

Scientists drilled deeper than ever beneath the West Antarctic Ice Sheet and found sediment and marine remains showing the area was once open ocean. The 23-million-year record offers key clues about past melting, helping researchers better predict how quickly the ice sheet could retreat and affect future global sea levels.

Scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory simulated one million potential satellite orbits between Earth and the Moon to assess long-term stability. Fewer than 10% remained stable over six years, highlighting the challenges of operating in cislunar space. Yet the results identified roughly 97,000 viable orbits, offering valuable options for future missions. The massive computation, completed in days using parallel supercomputers, provides a new roadmap for navigating the increasingly strategic Earth–Moon environment.

Astronomers have identified CDG-2, a faint galaxy in the Perseus cluster that appears to be composed almost entirely of dark matter. Located 300 million light-years from Earth, it was discovered by tracking globular star clusters using data from Hubble, Euclid, and Subaru telescopes. Scientists estimate that about 99% of its total mass is dark matter.

Boeing’s Starliner test flight has been reclassified by NASA as a Type A mishap after propulsion anomalies extended the mission from days to 93 days. Helium leaks and thruster failures during docking raised safety concerns and exposed technical and leadership shortcomings. An investigation issued 61 recommendations, and NASA says no additional crews will fly aboard Starliner until all issues are fully resolved and corrective measures are implemented before certification.

A new global map of small mare ridges suggests the Moon’s tectonic activity is younger and more widespread than previously believed. Researchers identified more than 1,100 previously unknown ridges, showing the lunar crust is still shrinking. These features, formed by thrust faults similar to lobate scarps, indicate moonquakes could occur across much broader regions. The findings may reshape how space agencies assess seismic risks for future lunar missions, including Artemis.

Microsoft’s Project Silica demonstrates that digital data can be stored in ordinary borosilicate glass for over 10,000 years. Using femtosecond lasers, researchers encode information as microscopic 3D voxels, achieving densities of 4.8 terabytes on a 2mm sheet. Unlike magnetic tapes or hard drives that degrade within decades, glass resists heat, moisture, and dust. Designed for long-term archives rather than everyday storage, this breakthrough could preserve cultural and scientific records for millennia.
New research suggests Saturn’s largest moon Titan and its iconic rings may share a violent origin. Simulations indicate Titan formed after a massive collision between two moons about 100 to 200 million years ago, resurfacing Titan and altering its orbit. The resulting instability likely shattered smaller moons, sending icy debris inward to create Saturn’s surprisingly young rings. Scientists say future missions could uncover evidence confirming this dramatic chapter in Saturn’s history.

Physicists have proposed a new concept called spacetime quasicrystals, orderly structures that never repeat but exist across space and time. If proven, they could help explain the universe’s deep structure, quantum gravity, and hidden dimensions, while preserving key laws of relativity even at extremely small scales.

ESA’s CHEOPS mission has uncovered a surprising rocky planet at the outer edge of the LHS 1903 system. Located 116 light-years away, the discovery defies expectations that outer planets are gas giants. Scientists say the finding offers rare evidence that planets can form in gas-depleted environments, challenging current planetary formation models.

Scientists have detected a possible ultra-fast pulsar spinning every 8.19 milliseconds near the Milky Way’s central black hole. If confirmed, this rare object could act as a precise cosmic clock, helping researchers study how gravity behaves in extreme environments and offering a powerful new way to test Einstein’s theory of general relativity near a supermassive black hole.

New research suggests the Universe’s expansion could eventually reverse, leading to a dramatic “Big Crunch.” By analyzing dark energy survey data, scientists propose expansion may stop in about 11 billion years before contraction begins. The model predicts a final cosmic collapse roughly 20 billion years from now, though uncertainties remain and future observations will test it.

Astronomers have identified two merging supermassive black hole systems named Gondor and Rohan using a new method combining quasars and gravitational wave background signals. The discovery offers a fresh way to map black hole mergers and understand galaxy evolution and cosmic gravitational waves in a clearer and more systematic manner.

A new Hubble image reveals twin beams blasting from a hidden dying star inside the Egg Nebula, a rare pre-planetary phase. The symmetrical arcs and glowing lobes show how Sun-like stars shed dust and gas before forming planetary nebulae, offering scientists a rare glimpse into stellar evolution.

Astronomers are closely tracking the bright green comet C/2024 E1 as it approaches Earth and prepares for a future escape from the solar system. Originating from the distant Oort Cloud, the city-sized comet is on a hyperbolic path and is expected to be permanently ejected after its close solar encounter, similar to the interstellar object 3I/ATLAS.

NASA is analysing data from a recent Artemis II confidence test that examined the SLS liquid hydrogen tank and replaced seals. Despite a ground equipment flow issue, engineers gathered critical performance data and will inspect systems before scheduling the next wet dress rehearsal, with March still considered the earliest possible launch window.

Scientists have refined Jupiter’s size and shape using modern radio signal observations, finding the giant planet slightly smaller and more flattened than earlier estimates. Though the difference is only a few kilometres, researchers say it greatly improves models of Jupiter’s interior, gravity, and atmospheric structure, offering deeper insights into gas giant formation and evolution across planetary systems.

NASA’s NEOWISE infrared telescope has provided striking evidence that a massive star in the Andromeda galaxy collapsed directly into a black hole without exploding as a supernova. The star, M31-2014-DS1, faded dramatically in visible light while leaving a faint infrared glow from surrounding dust. Astronomers say this rare “failed supernova” offers one of the clearest examples yet of a quiet stellar collapse in another galaxy.

Astronomers have discovered a rare inside-out planetary system around LHS 1903, where a rocky planet exists beyond gas giants. Using ESA’s CHEOPS telescope, researchers found evidence that planets formed one after another in a gas-depleted environment, challenging long-standing theories about how planetary systems form and evolve across the galaxy.

NASA has successfully flown its 40-inch CATNLF laminar-flow wing model aboard an F-15B aircraft in January 2026. The test confirmed the drag-reducing design performs safely in flight. By maintaining smooth airflow over wings, the technology could improve fuel efficiency by up to 10 percent, lowering airline costs and reducing carbon emissions significantly.

NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has released a striking new image of the Egg Nebula, capturing a Sun-like star in its brief pre-planetary phase. Twin beams of light pierce glowing shells of dust and gas, offering astronomers a rare close-up view of stellar death about 1,000 light-years from Earth.

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has revealed early galaxies that appear almost as old as the universe itself. By analyzing 31 galaxies at high redshift, researchers estimated stellar ages of around 600 million years—close to the universe’s age at that epoch. One galaxy may even seem older than the universe, posing a potential challenge to the standard Lambda-CDM cosmological model if confirmed.

NASA’s SPHEREx telescope captured a dramatic outburst from interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS after its close solar flyby in October 2025. Infrared observations in December revealed water vapor, carbon dioxide, methanol, methane, and cyanide erupting from the comet’s nucleus. Scientists say the chemical makeup suggests formation in a relatively warm environment beyond our solar system. The rare detection provides valuable insight into the composition and thermal history of material formed around another distant star system.

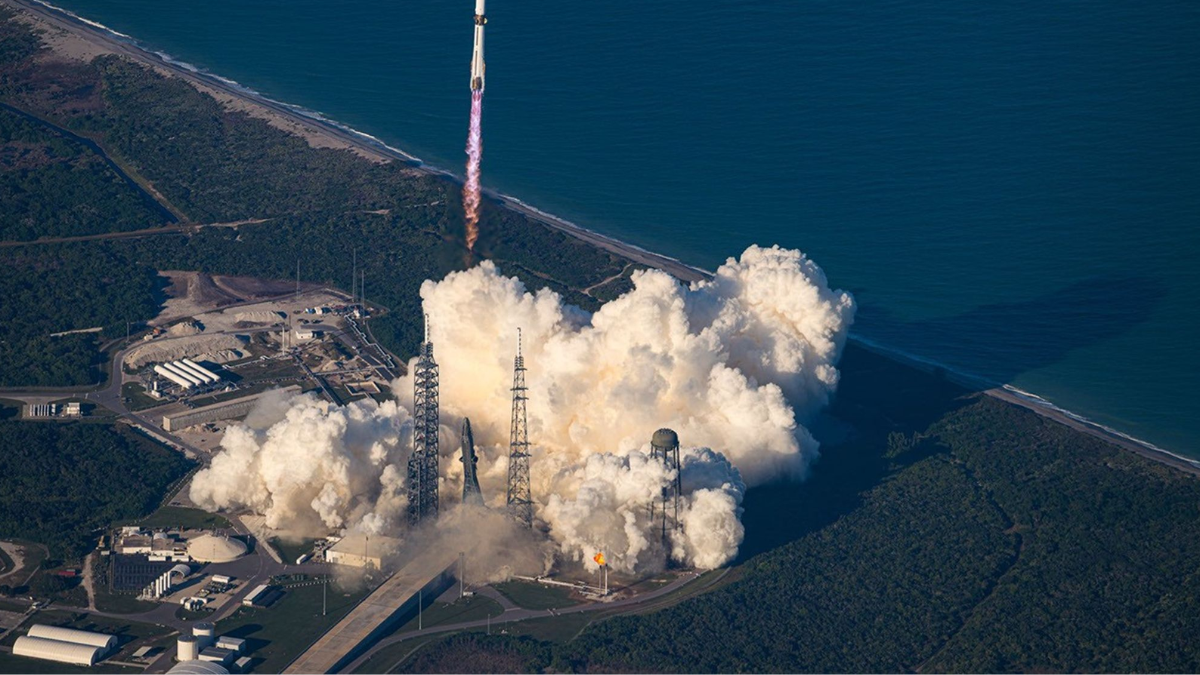
NASA and SpaceX have delayed the Crew-12 mission to the International Space Station because of unfavorable weather expected at Cape Canaveral. The launch is now targeted for February 12, with four astronauts waiting in quarantine as teams prepare the Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft for the next launch window.

Scientists analysing NASA’s Magellan radar data have identified signs of a vast underground lava tunnel on Venus. If confirmed, it would be only the second such structure found on the planet, challenging the belief that Venus is geologically inactive and opening new possibilities for studying its volcanic past.

A new theoretical study suggests dark matter may not exist, proposing instead that gravity behaves differently across vast cosmic distances. By modifying how gravity weakens over scale, the research explains galaxy rotation and lensing effects without unseen particles, raising questions about long-standing cosmological models and inviting a fresh look at gravity’s hidden complexity.

NASA’s SPHEREx telescope has observed interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS unexpectedly brightening as it leaves the solar system. The comet released water vapour, carbon dioxide, and organic compounds months after its closest solar approach. Scientists say the findings provide a rare chemical snapshot of material formed around another star, helping compare planetary ingredients across the galaxy.

NASA’s GNEISS mission will launch from Alaska in early 2026 to probe the electric currents that drive auroras. Two rockets will fly through glowing auroral arcs, releasing sub-payloads whose radio signals act like a CT scan. By mapping electron density and direction, scientists aim to improve space weather forecasting and better protect satellites and communication systems during periods of intense solar activity affecting Earth and modern technological infrastructure worldwide operations.

The James Webb Space Telescope has discovered MoM-z14, the most distant galaxy ever observed, dating to just 280 million years after the Big Bang. The galaxy’s brightness, chemical richness, and structure challenge existing theories of early cosmic evolution. Scientists say the finding highlights a growing gap between models and observations of the young universe.

A new study suggests dark matter may not exist. Physicist Naman Kumar proposes gravity weakens differently across vast distances, following a 1/r rule. This modified gravity model reproduces galaxy rotation curves using only visible matter, challenging long-held assumptions about unseen mass in the universe, and reshaping theories of cosmic structure formation.

NASA’s GNEISS mission will launch from Alaska in early 2026 to probe the electric currents that drive auroras. Two rockets will fly through glowing auroral arcs, releasing sub-payloads whose radio signals act like a CT scan. By mapping electron density and direction, scientists aim to improve space weather forecasting and better protect satellites and communication systems during periods of intense solar activity affecting Earth and modern technological infrastructure worldwide operations.

NASA’s Curiosity rover has resumed science operations after solar conjunction, returning to a previous drill site for a rare organic chemistry experiment. Using its final supply of TMAH, Curiosity will analyse Martian rock samples for signs of organic molecules while also monitoring dust and atmospheric conditions inside Gale Crater.

A mysterious neutrino detected in 2023 may be debris from an exploding primordial black hole. Scientists say the ultra-energetic particle defies known cosmic sources and could represent Hawking radiation, offering rare insight into early-universe physics and the possible nature of dark matter while challenging theories of black holes and cosmology.

The James Webb Space Telescope has discovered the most distant galaxy ever observed, JADES-GS-z14-0, seen as it existed just 300 million years after the Big Bang. Its unexpected brightness and chemical complexity suggest rapid early star formation, challenging long-standing theories about how the first galaxies evolved in the early universe.

Blue Origin has announced a temporary halt to flights of its New Shepard spacecraft, pausing its suborbital space tourism business for at least two years. The company says the decision will free resources to accelerate development of its Blue Moon lunar lander for NASA’s Artemis programme, including robotic tests and a planned crewed Moon landing later this decade as part of a broader shift toward deep-space exploration and infrastructure development.

NASA’s Perseverance rover has achieved a major milestone by navigating Martian terrain using artificial intelligence alone. In December 2025, AI-generated routes guided the rover safely across Jezero Crater, proving that autonomous navigation can dramatically speed up exploration and increase scientific returns on future planetary missions.

Japan’s XRISM X-ray observatory has delivered the first detailed maps of hot gas swirling around supermassive black holes in the Virgo and Perseus galaxy clusters. The data reveal intense turbulence, like cosmic storms driven by black hole jets. This churning heats the gas, stopping it from cooling and collapsing into new stars, explaining why cluster cores remain surprisingly star-poor. These findings reshape our understanding of how galaxies evolve.

Artificial intelligence has combed through decades of Hubble Space Telescope data, revealing hundreds of unusual celestial objects that astronomers had missed. ESA’s AnomalyMatch neural network scanned around 100 million image cutouts in just days, flagging more than 1,300 anomalies. Among them are colliding galaxies, rare gravitational lenses, and jellyfish galaxies, demonstrating how AI can rapidly unlock discoveries hidden within vast astronomical archives. The project highlights a new era where machines partner with scientists to explore the universe efficiently and faster.

A rapidly expanding sunspot has transformed the Sun into a solar flare powerhouse, producing more than 20 mid-level flares and several extreme eruptions in just one day. As the region now faces Earth, scientists are tracking potential radio blackouts, satellite interference, and dazzling auroras caused by incoming solar storms.

NASA’s Mars rover, Perseverance, recently completed its first drive using commands shared by Anthropic’s artificial intelligence (AI) chatbot, Claude. The milestone marks the first time a generative AI model has played a direct role in planning a rover’s movement on another planet. The drive took place on January 27, with Claude delivering high-level navigation instructions that were translated into precise waypoints before transmission to Mars.

Scientists have identified a natural “cosmic clock” inside zircon crystals that can date Earth’s surface processes over millions of years. By measuring cosmogenic krypton created by cosmic rays, researchers reconstructed erosion rates in southern Australia, revealing an exceptionally stable landscape shaped slowly over 40 million years and explaining the region’s zircon-rich sands.

NASA has selected Axiom Space to conduct its fifth private astronaut mission to the International Space Station. Launching in early 2027, Axiom Mission 5 will carry up to four private astronauts for a two-week stay, supporting NASA’s push toward a commercial future in low Earth orbit.

James Webb Space Telescope observations reveal that the earliest supermassive black holes formed from massive gas clouds collapsing directly into heavy seeds. This process bypassed normal star formation, allowing black holes to reach millions of solar masses within just 200–500 million years after the Big Bang, solving a long-standing cosmic mystery about galaxy evolution, and early universe physics insights emerge.

Rocket Lab successfully launched South Korea’s NEONSAT-1A satellite on January 29, 2026, completing the delayed Bridging the Swarm mission from New Zealand. Deployed into a 540-kilometer orbit, the Earth-observation spacecraft will deliver near-real-time imagery to monitor natural disasters across the Korean Peninsula. The launch marked Rocket Lab’s second mission of 2026 and its 81st Electron flight overall, carrying advanced optical sensors for rapid emergency response and environmental monitoring support efforts.

Astronomers have directly linked the supermassive black hole M87* to its enormous plasma jet using new Event Horizon Telescope data. The findings reveal where the jet originates near the black hole’s shadow, providing crucial insight into how black holes launch matter at nearly the speed of light.

Scientists studying archival Galileo spacecraft data have identified ammonia-bearing compounds on Europa for the first time. The ammonia appears along surface cracks, indicating recent transport from the moon’s subsurface ocean. Because ammonia contains nitrogen and degrades quickly under radiation, its presence strengthens Europa’s status as a promising target in the search for extraterrestrial life.